Identifying Policy Targets For Sustainable Agro-Processing Business In India’s Uttarakhand – Analysis
The industrial policy of Uttarakhand since its inception have endeavored to ensure fast, stable and sustainable industrial development in the state. The revival and growth of traditional industries with the objective of economic growth of local mountainous and hill areas was the primary target of industrial policy of the state.
There are many factors that have contributed to the slow economic growth of Uttarakhand. Slow industrial growth is among them as the major factor that have contributed a lot. However, the geographical features and agro-economic conditions of the state is such that it is most suitable for development of agro-processing units that can have profound impact to enhance economic growth of the state.
Potential
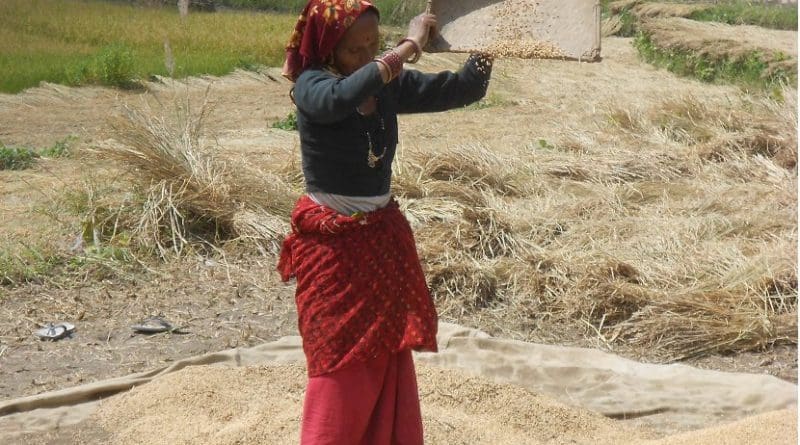
The state of Uttarakhand is observed with large variation in agro-climate which is suitable for cultivation of variety of crops. The diverse agro-climatic conditions of the state not only provide a unique advantage but also a competitive edge over other states in production of vegetables and fruits during off season. Around 23 percent of gross cropped area of the state has been used to cultivate vegetables, fruits, and other crops.
There is diversity in crop rotation and agronomic practices which depends upon practices adopted in different zones due to diversity in climatic conditions. Sugarcane and food grain dominant the cropping pattern in tropical zone, whereas wheat and paddy dominant the cropping pattern in the sub-tropical zone. In the month of March paddy is sown where as it is harvested in September. Normally, the sowing season of wheat is the October and harvesting season is May.
Post harvesting of wheat is followed by sowing of pure crops or mixed crops of mandua, pulses or other crops. Fruit crops such as peach, pear and khumani are cultivated in the land unsuitable for cultivation of sugarcane and food grain. Horticultural crops, floriculture crops, medicinal, aromatic plants and off-season vegetables are observed to be cultivated in Uttarakhand largely. Kharif crop cultivation which needs very cold climate is observed in temperate zone. Thus, in line with this it can be observed from cropping pattern of Uttarakhand that adequate amounts of raw materials are available to run agro-processing units in the state.
Initiatives to establish small and medium size agro parks, fruits and vegetable based wineries, agri-export zone for agro based export, packaging industry, post-harvest management infrastructure, high quality horticulture farms, and post-harvest management infrastructure will certainly ensure sustainable running and management of agro-processing units in the state.
Challenges
The challenges that the state faces in agro-processing sector are enormous and reforms at policy level must be adopted to address these challenges. Some of the major challenges given below must not be overlooked before implementing any policies pertaining to promotion of agro-processing units in the state.
- Logistics, supply chains, storage and processing facilities
- Transport and communication in hill areas
- Inadequate no of packaging industry
- Inadequate irrigation infrastructure for agriculture
- Inadequate retail outlet for sale
- Inadequate export processing zones and export houses
Strengths
Uttarakhand with a relatively non-polluted atmosphere and blessed with rare diversity of flora and fauna have opportunity to get raw materials not only from agricultural sector but also from forest sector, some of the examples of which are rare species of aromatic and medicinal plants.
The state has almost a peaceful environment that can facilitate in sustainable industrial development. The most important advantage is that the national capital territory from Uttarakhand is only 5 to 8 hours away by train and only 35 minutes away by air.
Policy Targets
With these potentials, challenges and strengths in hand there is a need for sustainable agro-processing business in Uttarakhand state. The success of sustainable agro-processing business rests upon many policy targets to meet, the major targets among them are:
- To make Uttarakhand a world class agro-processing business hub.
- To address the challenges, involve with agro-processing business associated at various stages.
- To maintain sustainable agro-processing business while preserving the Himalayan ecosystems and biodiversity.
- To generate sufficient employment opportunities for inhabitants of Uttarakhand with sustainable agro-processing business.
Conclusion and Policy Implications
There are ample opportunities in the state for agro-processing business so far as the availability of agricultural raw materials and forest products are concerned. However, these opportunities to promote agro-processing business are not free from challenges such as logistics, supply chains, storage and processing facilities; transport and communication in hill areas; inadequate no of packaging industry; inadequate irrigation infrastructure for agriculture; inadequate retail outlet for sale and inadequate export processing zones and export houses.
Thus in front of us there are many policy targets, the major targets among them are to make Uttarakhand a world class agro-processing business hub; to address the challenges, involve with agro-processing business associated at various stages; to maintain sustainable agro-processing business while preserving the Himalayan ecosystems and biodiversity; and to generate sufficient employment opportunities for inhabitants of Uttarakhand with sustainable agro-processing business. In order to meet these policy targets there is a need for academic and policy research with support from policy think tanks and public authorities to prepare a framework and formulate holistic and integrated approach for sustainable development of agro-processing sector in the state.
*Dr. Narendra N. Dalei, Assistant Professor (Sr. Scale), Department of Economics, School of Business, University of Petroleum and Energy Studies, Dehradun (India)

