China Struggles With Belt And Road Pushback – Analysis
China, in an implicit recognition that at least some of its Belt and Road-related projects risk trapping target countries in debt or fail to meet their needs, has conceded that adjustments may be necessary.
“It’s normal and understandable that development focus can change at different stages in different countries, especially with changes in government. So China can also make some strategic adjustments when cooperating with these countries, but it’s definitely not a reconsideration of the B&R (Belt and Road) initiative,” Wang Jun, deputy director of the Department of Information at the China Center for International Economic Exchanges told the Chinese Communist Party’s Global Times newspaper.
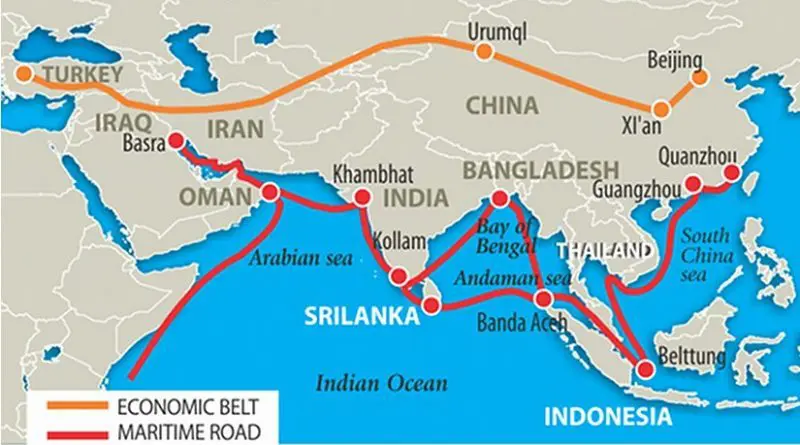
The Chinese concession, initially made public in an August 27 speech by President Xi Jinping and reaffirmed by the Global Times. came in the same week that Pakistan during a visit of Chinese foreign minister Wang Yi demanded that China expand its US$50 billion plus investment in the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), the single largest country infrastructure investment related to the People’s Republic’s Belt and Road initiative, to include manufacturing and poverty reduction projects.
The change in China’s approach towards Belt and Road would in the case of Pakistan involve a substantial recast of CPEC that appeared to position Pakistan as a raw materials supplier for China, an export market for Chinese products and labour, and an experimental ground for the export of the surveillance state China is rolling out, particularly in its troubled north-western province of Xinjiang.
The focus of Chinese investment takes on added significance as Pakistan weighs options to solve its financial crisis, including a request for up to US$12 billion in assistance from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) that would involve a straightjacket for structural reform.
An IMF assistance package would require Pakistan to provide chapter and verse of the finances of Belt and Road-related projects that have so far been kept under wrap.
Mr. Wang, the foreign minister, seemed despite the statements suggesting change, cautious in his response to the Pakistani demands. He indicated that that expansion, if not re-orientation of CPEC, would not be immediate. “The two sides have agreed that the CPEC cooperation will gradually shift to industrial cooperation,” Mr. Wang said during his visit.
Pakistan was not the only country that was pushing back at China’s approach towards the Belt and Road. Nepal joined Pakistan last November in withdrawing from dam projects because of China’s commercial terms.
More recently, protests against the forced resettlement of eight Nepali villages have apparently persuaded CWE Investment Corporation, a subsidiary of China Three Gorges, to consider pulling out of a 750MW hydropower project. CWE said it was looking at cancelling the project because it was “financially unfeasible.”
Malaysian prime minister Mahathir Mohamad has suspended or cancelled US$26 billion in Chinese-funded projects since his election victory in May.
Similarly, Myanmar is negotiating a significant scaling back of a Chinese-funded port project on the Bay of Bengal from one that would cost US$ 7.3 billion to a more modest development that would cost US$1.3 billion in a bid to avoid shouldering an unsustainable debt.
China has written off an undisclosed amount of Tajik debt in exchange for ceding control of some 1,158 square kilometres of disputed territory close to the Central Asian nation’s border with China’s troubled north-western province of Xinjiang.
Zambia, following in the footsteps of Sri Lanka that was forced to give China a major stake in its port of Hambantota because it could not service its debt, saw itself this month left with no choice but to hand over control of its international airport as well as a state power company.
The Chinese concession also comes amid increased international attention on China’s crackdown on Turkic Muslims in Xinjiang, including, the roll-out of its 21st century Orwellian surveillance state.
The concession is part of a concerted effort to downplay the geopolitical nature of the Belt and Road initiative and stress its sustainable development and job creation aspects.
Ray Washburne, president and CEO of the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC), an intergovernmental agency that channels US private capital into overseas development projects, earlier depicted the Belt and Road initiative as a ploy to ingratiate itself with other countries by funding infrastructure projects.
China ”is not in it to help countries out, they’re in it to grab their assets,” Mr. Washburne said. He charged that China was intentionally plunging recipient countries into debt, then going after “their rare earths and minerals and things like that as collateral for their loans.”
That view persuaded Greenland this month to select a Danish rather than a Chinese company to build and upgrade three airports.
“The big fear is that even a small Chinese investment will amount to a large part of Greenland’s GDP, giving China an outsized influence that can be used for other purposes,” said Danish foreign and defence policy scholar Jon Rahbek-Clemmensen.
Mr. Rahbek-Clemmensen’s concern reflects a widespread belief that the sheer scale of Belt and Road, involving up to US$1 trillion in investments in scores of countries across the globe lends it significant geopolitical attributes irrespective of what Chinese leaders may have had in mind.
A recent study by the Washington-based Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) argued that the Belt and Road is driven by “interest groups within and outside China (that) are skewing President Xi’s signature foreign policy vision.” The study argued that the positioning of the initiative persuaded Chinese local and regional authorities as well as companies to brand their activities as Belt and Road-related to gain economic and political advantage.
Earlier, the Washington-based Center for Global Development warned that “there is…concern that debt problems will create an unfavourable degree of dependency on China as a creditor. Increasing debt, and China’s role in managing bilateral debt problems, has already exacerbated internal and bilateral tensions in some BRI (Belt and Road initiative) countries.”