Libyan Exports Rain On OPEC’s Parade – Analysis
By Todd Royal
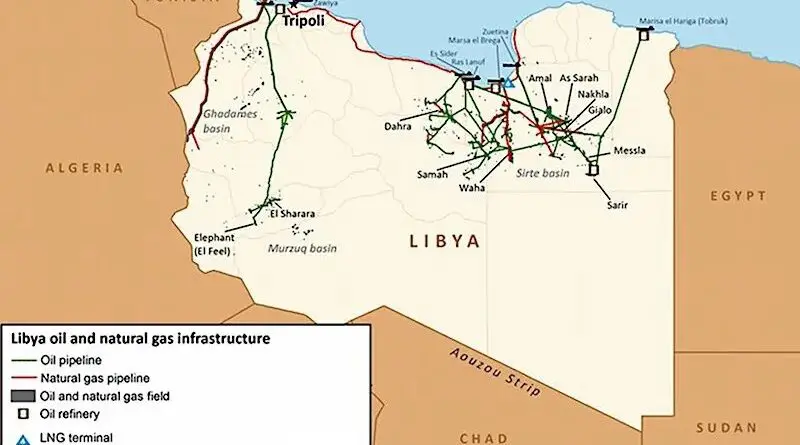
While Syria is the disaster of a generation, Libya isn’t far behind. Currently, Libya is upending global oil markets through increased oil production for export. This latest occurrence is overturning the OPEC production limit deal that exempts Libya, Nigeria, and Iraq.
While Nigeria and Iraq have their own domestic and geopolitical issues, it’s Libya and the various factions that should be of grave concern to the world community. Once NATO overthrew the Gaddafi regime without a nation-building plan in place, Libya became an attractive safe haven for ISIS and various other tribal factions warring over Libya’s fossil fuel resources, which represent billions a year in potential income.
The various armed factions (government-sponsored, Islamic, and military) are all vying for the opportunity and riches that comes with boosting Libya’s crude oil production to one million barrels per day (bpd) by the end of July. Recently, some of these factions signed an agreement with German Wintershall (GW) to get oil fields back online, adding another 160,000 bpd of output which would otherwise have been idle in the chaos following the invasion by Western powers.
Geopolitical forces were in play, but the various factions in question put their differences aside to put this deal in place; the result is that world oil markets are seeing more supply. The National Oil Corporation (NOC) and GW had formerly been locked in negotiations over disputed past payments for oil field services rendered. With these negotiations finally resolved, oil production has surged ahead crashing the OPEC deal, and the internal focus has shifted toward fighting ISIS instead of each other.
Reconciliations between rival factions have caused production to grow from 178,000 to over 902,000 bpd. Since oil accounts for an overwhelming majority of Libyan economic activity, this reconciliation has major geopolitical implications in the MENA region. New oil revenue allows the fledgling government to wage war against extremists, and set up a somewhat functional state in the midst of a troubled region.
Yet nothing is certain in Libya anymore, and the political system continues to be fractured as ever. If oil exports collapse over internal or external struggles, or Libyan militant groups decide to exert their own pressure on oil facilities, tensions will spike, output will drop, and government revenue will dry up. What Libya is then reduced to is an oil-producing state whose terminals, fields, and pipelines are at the frontlines of combating Islamic extremism and stopping the flow of immigrants from North Africa, the Middle East, and Central Asia that are overwhelming European policymakers.
Moreover, the Qatar crisis has exacerbated tensions in Libya between the various militias and groups vying for oil and political power. The eastern government in Libya joined with its financial backers in Egypt and the UAE by denouncing Qatar’s actions, and wanted oil companies operating in Qatar to cease and desist operations immediately.
These factions wanted Qatar Holding to stop doing business with a Swiss commodity trading giant, Glencore. However, Glencore has an oil export contract with the NOC as the only official and legal business allowed to export crude from Libya. Politics and business mixed together earlier this year when the eastern government and NOC chairman praised the Libyan National Army (LNA) in assisting the NOC to restore control over four key oil export terminals in the Libyan oil crescent.
The LNA is affiliated with the government in Benghazi, but given Libya’s internal political struggles, the situation on the ground can change quickly with regards to oil production and the fight against ISIS. Political and macroeconomic certainty is ever elusive in Libya since Gaddafi’s ouster.
In terms of Libya, the allegiances underpinning the Qatar crisis can be broken down into the following: Qatar supports Islamic militias in Misrata and other units loyal to Sadiq al-Ghariani, the Mufti of Qatar, but the UAE and Egypt support General Khalifa Haftar, the leader of the LNA who’s aligned with the government based in Tobruk.
Ever since the LNA took over oil terminals and relinquished control to the NOC, production disruptions have been less frequent. The NOC target of one million bpd seems achievable this summer unless ISIS is able to expand operations or another large-scale civil war erupts.
With Libyan oil production transforming back to higher, disruptive levels, the energy industry could be in for lower prices for the remainder of this year and next. As this Libyan revolution unfolds, energy investors can expect the unexpected, and changes in political leadership, economics, and various factions looking to destabilize the fragile government will have policymakers and business leaders treading lightly with regards to Libya.
The paradox is that, for starters, the resulting lower energy prices weaken both the Libyan economy and the economies of Arab states that rely on oil markets for geopolitical influence. With cheap and abundant oil resources since the 2014 crash, new policy responses are coming from nations like Saudi Arabia, which launched Vision 2030 and recently empowered the young son of King Salman as the next Saudi monarch. Other oil-reliant nations will have to respond as well if oil continues its downward trend.
Understanding Libya is a difficult assignment, but one thing is clear. As the country nears one million bpd in exports, any hope of stabilizing oil prices – and by extension politics in the MENA region – will remain elusive for years to come.