An Assessment Of China’s Economic Growth In The First Quarter – Analysis
By Anbound
By Chan Kung and He Jun*
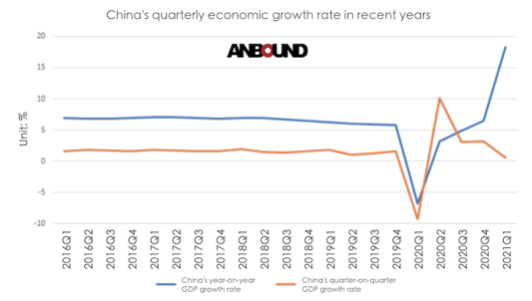
On April 16, China’s National Bureau of Statistics has released the economic data for the first quarter of 2021. Preliminary estimates show that China’s GDP in the first quarter was RMB 24.931 trillion, an increase of 18.3% year-on-year and 0.6% quarter-on-quarter at comparable prices. The first-quarter GDP was also 10.3% higher than the GDP in the first quarter of 2019, with a two-year average growth rate of 5.0%.
It should be pointed out that the 18.3% year-on-year GDP growth in the first quarter was an unusual growth under the low base effect. While the GDP growth in the first quarter was impressive, it was still slightly below market expectations of 20% growth. In particular, the economy grew by 0.6% quarter-on-quarter in the first quarter, 2.6 percentage points lower than the quarter-on-quarter growth rate in the fourth quarter of 2020, indicating a slowdown in the pace of economic recovery.
Taking the first quarter of 2019 as the base, China’s GDP growth averaged 5% over two years, and this is still lower than the 5.8% growth rate in the fourth quarter of 2019 before the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Data from the major sectors of the economy provides a more detailed picture of the economy’s performance in the first quarter.
In terms of industrial growth, in March, the value-added of the industrial enterprises above designated size grew by 14.1% year-on-year. In the first quarter, the value-added of the industrial enterprises above designated size grew by 24.5% year-on-year, up 14.0% compared with the same period in 2019, and the two-year average growth rate was 6.8%, close to the 6.9% growth rate at the end of 2019 before the outbreak of the pandemic. However, the year-on-year growth slowed to 14.1% in March, below the average market forecast of 15.4%. In particular, industrial growth slowed to a seasonally adjusted 0.6% quarter-on-quarter, the first deceleration since December 2020. Some market analysts believe that the industrial output in March did not continue the remarkably high growth in January-February is one of the reasons why the year-on-year GDP growth in the first quarter did not reach the 20% upper limit as expected by the market.
In terms of investment, from January to March, China’s fixed asset investment (excluding rural households) was RMB 9.5994 trillion, up 25.6% year-on-year and up 2.06% compared with October-December last year after seasonally adjusted; it was 6.0% higher than that from January to March in 2019, with an average growth rate of 2.9% in two years. Among them, private investment in fixed assets was RMB 5.5022 trillion (accounted for 57.3% of the total investment), up 26.0% year-on-year. On a month-on-month basis, investment in fixed assets (excluding rural households) rose 1.51% in March. By industry, the investment in the primary industry was RMB 236.2 billion, up 45.9% year-on-year; the investment in the secondary industry was RMB 2.792.9 trillion, up 27.8%; the investment in the tertiary industry reached RMB 6.5703 trillion, up 24.1%. It can be seen that the growth of investment in the first quarter has maintained relatively strong momentum. In addition to the significant year-on-year growth, investment has also maintained a significant quarter-on-quarter growth, and maintained positive growth in March.
Consumption growth, which was negative last year, turned positive in the first quarter of this year. In March, the total retail sales of consumer goods reached RMB 3.5484 trillion, a year-on-year increase of 34.2% (well above market expectations of 28%); it was 12.9% higher than that in March 2019, with an average growth rate of 6.3% in two years. After deducting price factors, the total retail sales of consumer goods in March 2021 increased by 33% in real terms, with an average growth of 4.4% in two years. On a month-on-month basis, the total retail sales of consumer goods increased by 1.75% in March. From January to March, the total retail sales of consumer goods reached RMB 10.5221 trillion, a year-on-year increase of 33.9%, with an average growth rate of 4.2% in two years; after seasonal adjustment, it increased by 1.86% compared with October to December last year. In terms of online retail sales, from January to March, China’s online retail sales reached RMB 2.8093 trillion, a year-on-year growth of 29.9% and an average growth of 13.5% in two years. Of this, online retail sales of physical goods reached RMB 2.3067 trillion, an increase of 25.8%, with an average growth of 15.4% in two years, accounting for 21.9% of the total retail sales of consumer goods. If retail consumption growth is sustained, it will provide important support for China’s economic recovery this year.
In terms of income and expenditure, the nationwide per capita disposable income has reached RMB 9,730 in the first quarter, a nominal increase of 13.7% year-on-year, with an average two-year growth of 7.0%, or a real increase of 13.7% year-on-year after deducting price factors, with an average two-year growth of 4.5%. In the first quarter, the growth rate of per capita disposable income has increased quarter by quarter, maintaining stable recovery growth, but it was still significantly lower than the economic growth rate in the same period. In terms of urban and rural areas, the per capita disposable income of urban households was RMB 13,120, a nominal increase of 12.27% year-on-year and a real increase of 12.3%; the per capita disposable income of rural households was RMB 5,398, a nominal increase of 16.3% year-on-year and a real increase of 16.3% after deducting price factors. In the first quarter, China’s per capita consumption expenditure reached RMB 5,978, a nominal increase of 17.6% year-on-year or a real increase of 17.6% after deducting price factors; it was 8.0% higher than that the first quarter of 2019 with two-year average growth of 3.9% or 1.4% after deducting price factors.
In terms of foreign trade, China’s merchandise imports and exports amounted to RMB 8.47 trillion in the first quarter of this year, up 29.2% year-on-year, according to the General Administration of Customs. Among them, exports grew 38.7% to RMB 4.61 trillion, imports grew 19.3% to RMB 3.86 trillion, and the trade surplus reached RMB 759.29 billion, an increase of 690.6%. In March, China’s dollar-denominated exports grew 30.6% year-on-year, down 30 percentage points from January-February, while dollar-denominated imports increased by 38.1%, up 15.9 percentage points from January-February. The trade surplus for the month was USD 13.8 billion, down USD 89.46 billion from January-February. In RMB terms, exports rose 20.7% in March from a year earlier, down 29.4 percentage points from January-February, while imports grew by 27.7%, up 13.2 percentage points from January-February. The trade surplus in the same month was RMB 87.98 billion, a decrease of RMB 587.88 billion. It can be seen that with the economic recovery at home and abroad, China’s imports and exports have seen significant growth. The growth rate of imports exceeds that of exports, showing the characteristic of China as the “world’s factory”.
Overall, China’s economy grew sharply in the first quarter as expected due to a low base effect. However, the growth rate was lower than the market had expected. As ANBOUND has pointed in the past, to fully understand the actual situation of China’s post-pandemic economic growth, one should look at the economic growth in the past three years as a whole. Therefore, China’s quarterly economic growth this year will be high at the beginning of the year, and it will be lower afterwards. It is expected that the economic growth over the next year or two will be significantly slower than that of this year.
It is also important to note that China can no longer be the star performer of the world’s major economies, as it was last year. As vaccines continue to roll out, the global economy will generally recover in 2021, with the U.S. economy in particular rebounding strongly. According to Federal Reserve’s officials, the U.S. economy is expected to grow by 6.5% this year, with the inflation rate rising to around 2.5% and the unemployment rate falling to around 5% by the end of the year. Other institutions expect the U.S. to be the locomotive of global economic growth this year, contributing more to global economic growth than China; the U.S. economy will still be able to grow at 3.5% by 2022.
Final Analysis Conclusion:
As both the world economy and the Chinese economy are on the track of recovery, the most crucial goal for the Chinese economy is not to pursue a single year’s growth, but to maintain stability for at least three years, while addressing its internal problems of the Chinese economy. In this regard, China’s macro policy is expected to focus on the twin goals of “stability” and “risk prevention,” and the pursuit of balanced growth.
*About the authors:
- Founder of Anbound Think Tank in 1993, Chan Kung is one of China’s renowned experts in information analysis. Most of Chan Kung‘s outstanding academic research activities are in economic information analysis, particularly in the area of public policy.
- Mr. He Jun takes the roles as Partner, Director of China Macro-Economic Research Team and Senior Researcher. His research field covers China’s macro-economy, energy industry and public policy.

