Healthy Consumption Growth Keeps US GDP Positive In Fourth Quarter – Analysis
By Dean Baker
The US economy grew 0.7 percent in the 4th quarter, bringing its rate for the full year (4th quarter to 4th quarter) to 1.8 percent. That is a substantial slowing from the 2.5 percent rates of the prior two years.
By far the major component boosting growth was consumption, which grew at a 2.2 percent annual rate, driven largely by continued strong growth in durable goods consumption, which grew at a 4.3 percent annual rate. Consumption of services grew at 2.0 percent annual rate and non-durables grew at just a 1.5 percent rate.
Housing was also a big contributor to growth, expanding at an 8.1 percent annual rate and adding 0.27 percentage points to growth. Housing growth has averaged 8.5 percent over the last seven quarters. While this component is likely to continue to grow in 2016, the pace will probably be somewhat slower.
Investment and trade were both big negatives in the quarter. The trade deficit, measured in constant dollars, increased by $20.4 billion in the quarter, subtracting 0.47 percentage points from growth. The trade deficit is likely to continue to grow in 2016 as the dollar has risen further and we probably have still not felt the full effects of the prior increase.
Spending on equipment and non-residential structures both fell in the quarter, subtracting 0.3 percentage points from growth. Equipment spending has been hard hit both due to the impact of the trade deficit on manufacturing and also due to the collapse of investment in energy related sectors. There has been some overbuilding in office buildings and retail space which could be a drag on non-residential construction in 2016.
Another factor depressing growth in the quarter was the slowing of inventory investment, which subtracted 0.45 percentage points from growth. The growth in final demand in the fourth quarter was 1.2 percent.
The government sector added modestly to growth, with a 2.7 percent increase in federal spending slightly offsetting a 0.6 percent fall in state and local spending. Both figures are slightly anomalous (federal spending is growing more slowly and state and local spending is growing), but the net impact on growth of 0.12 percentage points is roughly what we can expect in future quarters.
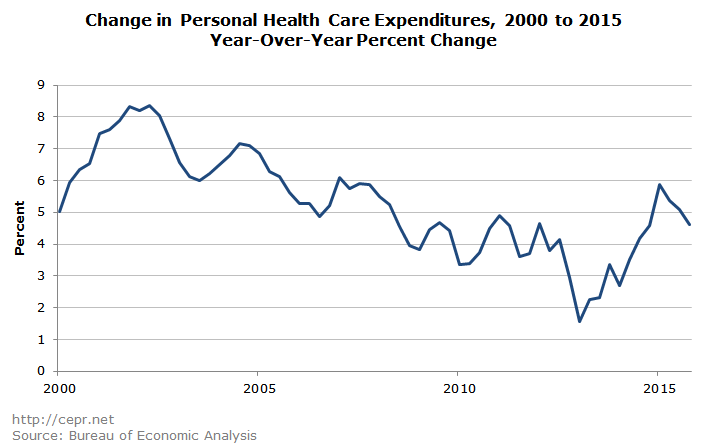
Health care spending continues to be very much under control. Spending on health care services, which accounts for the overwhelming majority of total health care spending, rose at a 5.2 percent nominal rate in the fourth quarter. This brings the increase over the last year to 4.8 percent.
Inflation continues to be nowhere in sight. The core PCE grew at just a 1.2 percent annual rate in the quarter, bringing the increase for the year to 1.4 percent, well below the Fed’s 2.0 percent target.
Non-farm business value-added grew at just a 0.1 percent annual rate. Given the strong growth in employment over the last three months of 2015, this implies that productivity growth will be negative for the quarter and barely positive for the year as a whole.
One of the striking aspects of the recovery had been the sharp and completely unpredicted collapse of productivity growth. This has been a positive in that employment growth would have been near zero if productivity growth had remained in a range of 1.5–2.0 percent over the last five years. On the other hand, if productivity growth remains stuck at the slow pace of the last five years, it will impose a serious limit on the ability to raise living standards.
A possible explanation is that the weak labor market itself is acting as a drag on productivity as workers are forced to take low-paying, low-productivity jobs. We will only know if this is true if the labor market tightens enough to give workers more bargaining power and the ability to move to higher paying jobs.
The overall picture of the economy going into 2016 is one of weak growth, albeit with little risk of recession. Consumption growth is likely to remain moderate, especially if energy prices stay low. Investment is likely to be a small negative in 2016 as is trade. However, residential construction and government spending will both be modest positives. The biggest risk is that a set of bad events elsewhere in the world could cause the trade deficit to deteriorate further.


The author stated a very important point about productivity. He thinks the collapse of productivity growth is contributing positively to employment growth. He also thinks that slow productivity growth puts limit on the ability to raising living standards. The author has not informed readers about the optimal outcome needed to generate more employment, higher wages, and higher standard of living. First, if productivity growth is collapsing and given the current wage level, then the unit labor cost will rise. This will hurt capitalist income share (or profit) as labor income share (wage) will increase. Under this condition, the Fed always responds by increasing the federal funds rate or the short-term interest rate, as was happened last December. Second, it is reasonable for the manufacturing sector to generate a higher rate of profit in order to increases real investments and expand productive capacity. The rise in real investments and productivity are the only way to counter the economic slowdown in the US economy. Third, the bigger risk does not come from external events in the world as the author thinks, but it actually comes from the US economy when the financiers (the new Jihadists) blow themselves out by the bubbles they have created and the huge wealth they have accumulated with the help of the Fed and the government.
Onward and upward!LOL