Sudan Is On The Brink Of A New Catastrophe – Analysis
By Martin Plaut
On Tuesday, December 19, Sudan’s second largest city, Wad Madani, fell to one of the most brutal armed groups worldwide. This made few headlines in a world obsessed with the fighting in Gaza.
The Sudanese war — which erupted in April this year — has pitted the Sudanese Armed Forces against the Rapid Support Forces (RSF). On the surface, it was no more than a quarrel between two generals. However, behind the military men are a range of outside forces. While the army has been the traditional bastion of the state, the RSF grew out of the notorious Janjaweed, a notorious Sudanese Arab militia charged with genocide for its activities in Sudan’s western region of Darfur.
As Kate Ferguson of Protection Approaches wrote:
“The RSF is the Janjaweed rebranded, the “devils on horseback” used by the Sudanese government from 2003 to implement widespread and systematic crimes against non-Arab communities across Darfur. The RSF was, and still is, commanded by Gen Mohamed Hamdan “Hemedti” Dagalo.”
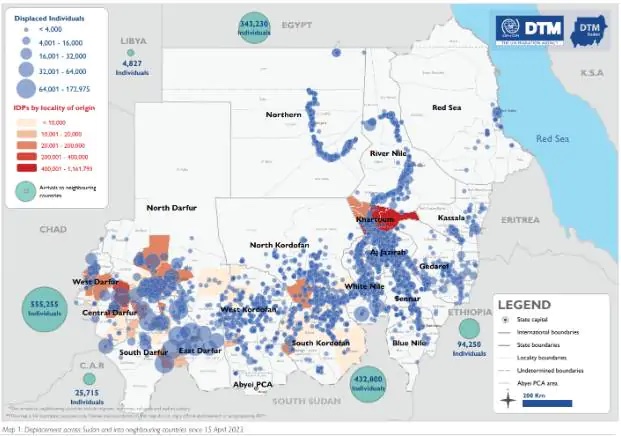
The war is a tragedy for the Sudanese people. It has forced an estimated 6.7 million people to flee from their homes. According toaid agencies, this is “the largest displacement crisis globally.” Although apparently no more than a regional issue, Sudan’s conflict has the potential to reshape the politics of the region, with implications for the entire Middle East.
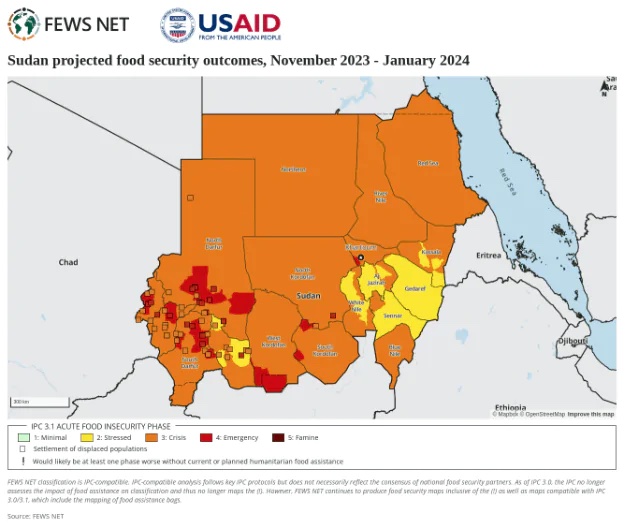
That reshaping might come later. At the moment, the humanitarian crisis is dire and can be grasped from two maps. The first map, by theInternational Organisation for Migration, shows where the population has fled.
The second map, by the Famine Early Warning System, shows just how close many Sudanese are to famine, having been forced off their lands. Over half the population — 25 million people (including 13 million children) — urgently need humanitarian assistance.
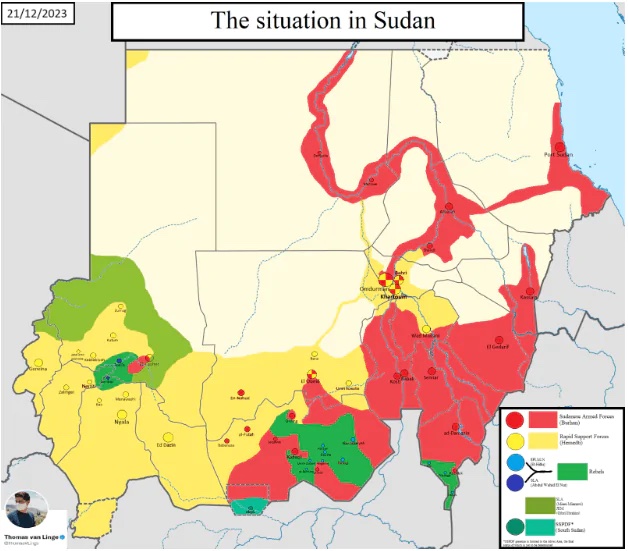
The fall of Wad Madani after three days of fighting left the RSF with a precious resource. Not only did it capture a city that was home to the army’s first infantry division, the RSF now holds the urban area to which most aid agencies decamped after the fighting erupted in Khartoum, the Sudanese capital. Now, the rebel RSF holds most of Khartoum and large parts of Darfur, while the Sudanese army, under General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, has had to decamp to the relative safety of Port Sudan.
Chatham House analysts neatly summed up the situation: “An effective partition has emerged in Sudan, with the army controlling the east and northeast and the RSF controlling much of the capital and west of the country.”
International forces fueling the conflict
The African Union (AU) and its regional body — the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) — have made little headway in attempting to end the fighting. South Sudan, Djibouti and Ethiopia are attempting to appoint a special envoy, but even if they manage to select an appropriate mediator, it is hard to see how this envoy will make progress. The much vaunted African Standby Force, on which the AU and the international community have spent vast sums of money, is yet to be deployed. Instead, the only viable peace talks have taken place in Jeddah, which indicates that the Arab world, not the AU, is playing a more significant role in Sudan.
The fighting between the Sudanese army and the RSF is backed by external supporters. Burhan and the army look north for support. Historically, most Sudanese have looked to Egypt for support. Burhan was trained in Egypt and is a regular guest of President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi, who has just won a third term in office. The Sudanese general can also rely on the Saudis for some backing. Also, the US gives Burhan and the army lukewarm support.
The reason US support is lukewarm is simple. President Joe Biden is bogged down by the Israel-Hamas conflict in Gaza. With his reelection bid kicking off, Biden has little time to concentrate on Sudan. This apparent indifference is a mistake. Alex de Waal arguesthat benign neglect does not serve Washington’s interests. The Sudanese crisis will only end when the US engages more robustly.
Note that Burhan and the army have a poor support base. The RSF is much better resourced. Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, generally referred to mononymously as Hemedti, leads the RSF. He is a former Janjaweed leader who was the deputy head of the Transitional Military Council following the 2019 Sudanese coup d’état. Hemedti has backers and the RSF has more money, men and motivation than the army.
Hemedti has links across the border in Chad, which he has exploited to the full. In fact, the RSF, is a revamped version of the Janjaweed and has terrorized Sudan. Its Arab fighters have attacked and killed African populations in Darfur.
Hemedti has also taken control of the resources of the region in general, and its gold mines in particular. He was encouraged and supported by Russia’s Wagner Group, which has taken a share of the spoils in return for supplying weapons to the RSF. This supply was tracked and traced by CNN. There is now clear evidence that the Wagner Group has been providing the RSF with missiles. Sudanese gold, flown out of Libya and on to the Russian base at Latakia paid for the weapons. This gold has not only funded Wagner, but also President Vladimir Putin’s war in Ukraine.
Apart from Russia’s Wagner Group, the UAE is the RSF’s other major backer. The Sudanese army says it has “information from intelligence, military intelligence, and the diplomatic circuit that the UAE sends planes to support the Janjaweed.” The UAE has established hospitals in Chad to provide treatment for refugees fleeing from the fighting. Although the UAE denies it, there is a widespread belief that the aid is little more than a front for weapons supplies for the RSF.
Uganda is seen as an alternative route for the UAE’s support for Hemedti’s operations. Reportedly, when a plane landed at Uganda’s main airport Entebbe in June this year, its flight documents said it was carrying humanitarian aid sent by the UAE for Sudanese refugees. Instead, “Ugandan officials said they found dozens of green plastic crates in the plane’s cargo hold filled with ammunition, assault rifles and other small arms.”
Little surprise then that the Sudanese army declared 15 members of the UAE embassy persona non grata on December 11. But outgunned and with limited diplomatic support, Burhan’s position appears to be weakening. At this moment there seems little chance of his allies providing the Sudanese army with the backing they require to hold off the Hemedti-led RSF. If Hemedti was to succeed in his campaign to oust the Sudanese military (and he is still some way from that objective) it would be a huge boost for his backers. The UAE would have extended its influence deep into Africa. The Wagner Group would have enhanced its operations across a vast swathe the Sahel. Hemedti’s victory would strengthen Putin’s influence and finances. It would also be a major blow to the US and the West. Already the Wagner Group has effectively chased the French out of Mali. Needless to say, a great deal is riding on the outcome of the Sudanese civil war. The future not only of a country but also of an entire region is at stake.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Fair Observer’s editorial policy.
- About the author: Born in South Africa, Martin Plaut is currently senior research fellow at the Institute of Commonwealth Studies and holds the same post with King’s College London. He studied at the Universities of Cape Town, Witwatersrand and Warwick before joining the Labour Party as secretary on Africa and the Middle East. In 1984 he joined the BBC, working primarily on Africa. He became Africa editor at World Service News, retiring in 2013. Plaut has advised the British and American governments, as well as the European Parliament. He has published widely on the Horn of Africa and southern Africa.
- Source: This article was published by Fair Observer